What is Part O?
Over the past year, Part O has steadily made its presence felt in the planning and design stages of residential projects. Most residential designers and developers will now have some experience of it.
Part O was introduced to the Building Regulations to address the increasing problem of overheating in new residential properties. The problem has escalated over the last couple of decades as buildings have become increasingly insulated, more airtight, and equipped with lightweight facades featuring expansive glazing. Simultaneously, rising global temperatures have exacerbated external heat levels. (We have all probably had some experience of trying to relax or sleep in an overheated room – it’s not pleasant!)
Part O contains specific design requirements for the control of overheating that now must be complied with. There are two routes to compliance, a simplified method and a detailed method. We provided a webinar discussing the criteria in detail at the time when Part O was introduced. If you are interested, the relevant section of the webinar can be seen here.

Noise requirements
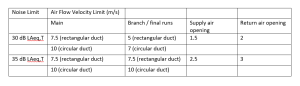
Regardless of whether compliance is sought via the simple or detailed method, Part O contains a separate noise-related requirement that if noise levels will exceed defined levels in bedrooms at night with their windows open, then the dwellings must be designed so that they will pass the overheating assessment with the bedroom windows closed.
The aim of this requirement is to help avoid the situation where residents are forced to open windows and expose themselves to high noise levels that may disrupt sleep quality – a crucial consideration for health and well-being. (We’ve all probably experienced the detrimental effects of noise on a good night’s sleep!)
The noise limits in Part O are very low, and therefore we have seen that for most new developments, even those in areas we would considered to be relatively quiet, there have been restrictions on the opening of bedroom windows for the overheating assessment.
In nearly all cases where bedroom windows have needed to be kept closed, the bedrooms have failed the overheating assessment initially and additional mitigation has been necessary.
It’s worth noting that ongoing industry discussions are advocating for the relaxation of the stringent noise limits in Part O due to the absence of sufficient technical evidence supporting their current severity. Stay tuned to our LinkedIn page for updates on this front.

Solutions
The ideal solution for Part O compliance is to design residential developments so that all bedrooms have access to a window on a quiet facade. Occupants will then be able to keep the windows open without compromising internal noise levels.
However, this is often not possible due to site locations and other design considerations/limitations, particularly the need to optimise the value of the site and therefore achieve a good density of dwellings. The layout of the development is also normally already fixed by a planning consent and therefore there is little to no flexibility in the development layout.
Furthermore, as above, the noise criteria in Part O are also very low and therefore we regularly see exceedances on sites that would otherwise be thought of as relatively quiet.
In these cases, modifications must normally be made to the design of the development to reduce overheating. From the projects we have worked on since Part O’s introduction (roughly 40 separate developments), the following additional mitigation have been chosen for affected dwellings/bedrooms to achieve compliance (from most common to least common):
- Low g value glazing (including triple glazing)
- Enhanced mechanical ventilation (either MVHR systems, or in some cases purge fans to affected rooms)
- Tempered air (normally a cooling unit attached to an MVHR system)
- Full comfort cooling (i.e. air conditioning)
Blinds are known to be effective at helping to mitigate overheating however only integral blinds (i.e. those where the blind is within the glazing) are officially allowed for Part O compliance. These are expensive and generally considered to be undesirable due to maintenance, cleaning etc.
Solar shading is an excellent solution to overheating however needs to be factored into the design of buildings early on and prior to the planning application. We anticipate a growing use of solar shading in development design over the next 5-10 years as shading products improve, and architects and developers increasingly recognize their broader benefits.
It is also worth saying that we have seen a large variation in attitudes from Building Control Officers in relation to the need to achieve full compliance with Part O. Some officers have taken a more pragmatic view on achieving full compliance given some of the practical difficulties and conflicts with other building regulations requirements (e.g. security, max. window openings, etc). As with all new and complicated regulations, individual officers’ understanding of the requirements can also vary.
How to avoid issues on your projects
Given the cost and design implications of the mitigation measures listed above, we would always recommend that developers and design teams start thinking about Part O compliance at the earliest stages of design (i.e. RIBA Stages 1 & 2). This will ensure that any necessary mitigation is minimised and/or costed into the project as appropriate. It will also allow measures such as solar shading to be considered.
Having worked on a number of projects to date (and being very familiar with noise affecting developments generally) we are more that happy to give initial advice on where Part O noise limits are likely to be exceeded and provide free outline advice on possible solutions. Please do get in touch if you have a project you would like us to look at for you.
We would also recommend early consultation with Building Control to establish their views.
Summary
- Part O compliance has significantly impacted the design of new residential developments, particularly those situated in urban areas where noise levels are typically higher.
- Addressing compliance early in the design process allows for more accurate budgeting and better optimisation of treatments.
- We are available to provide initial advice on where Part O noise limits are likely to be exceeded and outline guidance on possible solutions for budgeting and design coordination.
We hope you find this article helpful. Should you require more detailed information, we can offer comprehensive CPDs on Part O. Additionally, remember to follow us on LinkedIn to stay informed about developments in Part O and other matters related to acoustics and air quality.










 Construction noise monitoring at Ocean Village, Southampton for Bouygues
Construction noise monitoring at Ocean Village, Southampton for Bouygues