- a
- b
- c
- d
- e
- f
- g
- h
- i
- j
- k
- l
- m
- n
- o
- p
- q
- r
- s
- t
- u
- v
- w
- x
- y
- z
a
ADMS
Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling System
AURN
Automatic Urban and Rural (air quality monitoring) Network, managed by contractors on behalf of Defra.
Accuracy
A measure of how well a set of data fits the true value.
Adjustment
Robust correction of modelled results to account for uncertainties in the model.
Air Quality Action Plan (AQAP)
Air Quality Action Plans provide the mechanism by which local authorities, in collaboration with national agencies and others, state their intentions for working towards the air quality objectives using the powers they have available.
Air Quality Annual Status Report (ASR)
A document produced by local authorities in the UK to report on air quality within their jurisdiction. These reports are part of the LAQM framework and are required under the Environment Act 1995.
Air Quality Assessment (AQA)
A comprehensive evaluation of the levels and sources of air pollution in a specific area, to determine whether air quality meets established health and environmental standards. These assessments are crucial for informing policy decisions, planning new developments, and protecting public health and the environment.
Air Quality Management Area (AQMA)
An Air Quality Management Area (AQMA) is declared for an area where a local air quality is unlikely to meet the Government’s national air quality objectives. Once an AQMA has been declared, the local authority has to carry out further work to monitor the air quality in the area and identify what action can be taken to improve it.
Air Quality Neutral (AQN)
A term for developments that do not contribute to air pollution beyond allowable benchmarks.
Air Quality Objective (AQO)
Policy target generally expressed as a maximum ambient concentration to be achieved, either without exception or with a permitted number of exceedances within a specific timescale (see also air quality standard).
Air Quality Standard
The concentrations of pollutants in the atmosphere which can broadly be taken to achieve a certain level of environmental quality. The standards are based on the assessment of the effects of each pollutant on human health including the effects on sensitive subgroups (see also air quality objective).
Ambient Air
Outdoor air in the troposphere, excluding workplace air.
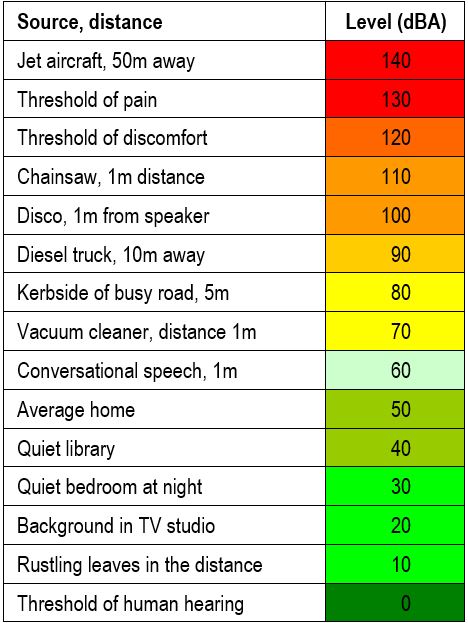
Ambient Sound (as used in BS4142:2014)
The sound that comprises the total sound for a specific situation and time (e.g. distant road traffic + wildlife + air conditioning unit)
Annoyance
Loss of amenity due to dust, odour or pollution often related to people making complaints, but not necessarily sufficient to be a legal nuisance.
Annual Average Daily Traffic (AADT)
The traffic flow for a 24-hour period, averaged over a year.
Annual Average Weekday Traffic (AAWT)
The total volume of vehicle traffic, weekdays only, on a road or motorway for a year divided by the number weekdays in the year; a measurement of how busy a road is during the working week.
Annual Mean
The average (mean) of the concentrations measured for each pollutant for a specific year.